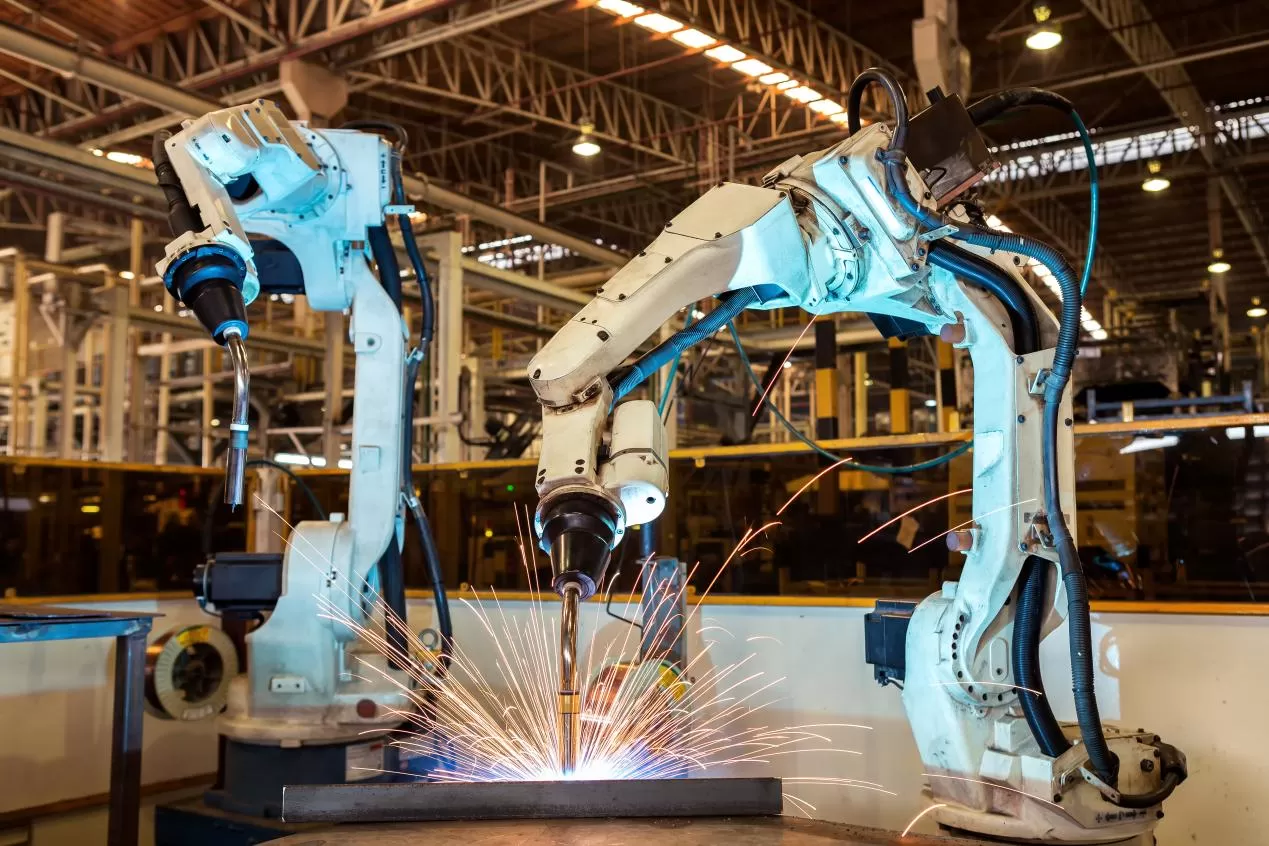

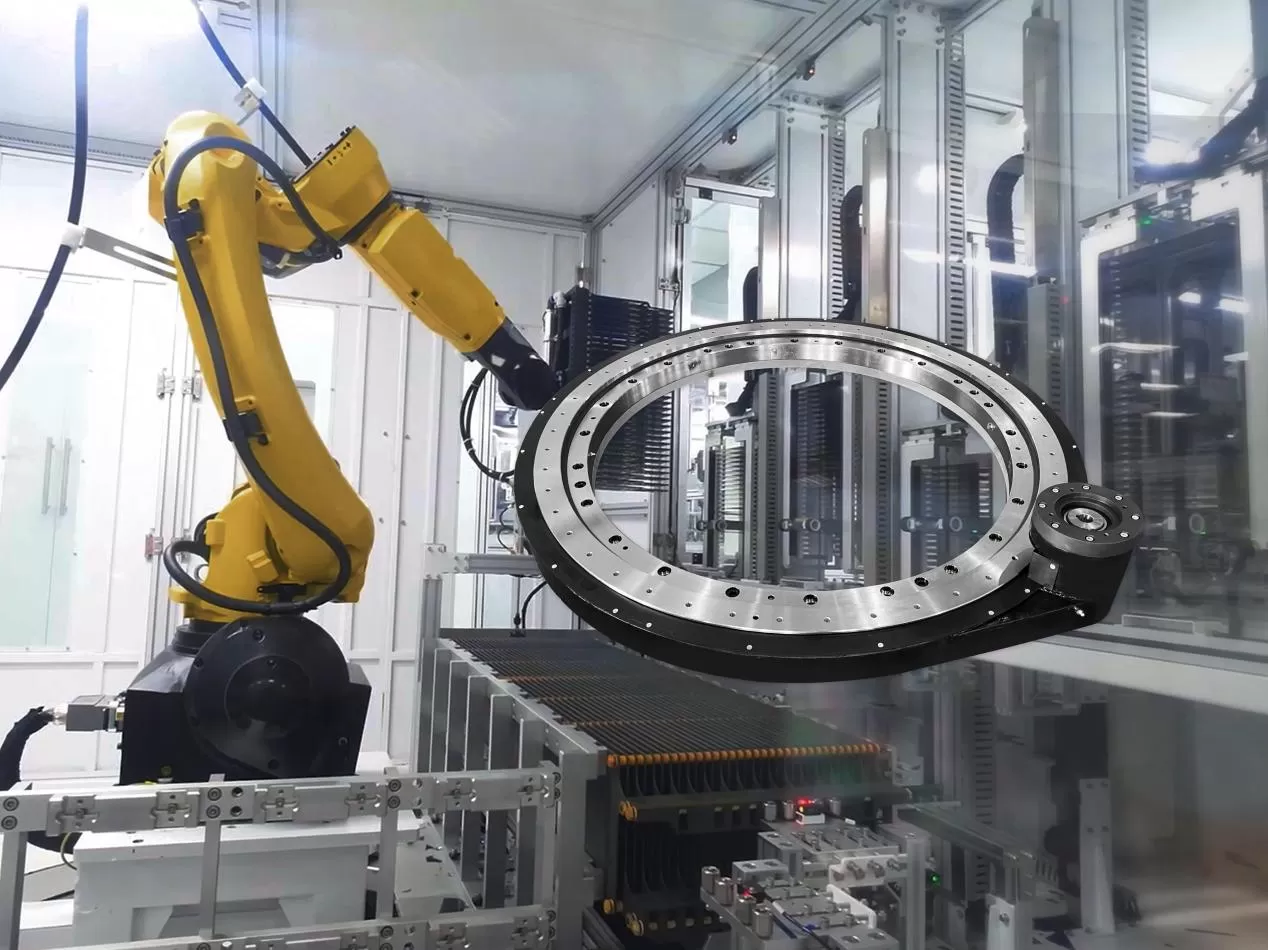
In high-end equipment manufacturing fields such as automobile production, engineering machinery, and aerospace, the operational accuracy, environmental adaptability, and installation flexibility of welding robots directly determine the stability of welding processes and product qualification rates. As the core transmission component for joint rotation and base positioning of robots, the spur gear slew drive has emerged as a key adaptive solution for the upgrading and iteration of welding robots by virtue of its core advantages of high protection, high rotational speed, high precision, and high integration, providing reliable transmission support for complex welding scenarios.
The spur gear slew drive adopts a fully sealed structural design with a protection rating of up to IP53, which can effectively resist the intrusion of pollutants such as welding spatter, dust, and coolant in welding scenarios, while also featuring excellent waterproof and dustproof performance. Even during long-term operation in dusty and high-humidity welding workshops, it can prevent corrosion and jamming of internal gear components, significantly reduce equipment maintenance frequency, and ensure the continuous and stable operation of welding robots.
Tailored to the light-load operating conditions of welding robots, the spur gear slew drive features an optimized transmission structure with a maximum rotational speed of 20 rpm. Compared with traditional transmission components, it delivers faster response speed, enabling robot welding torches to quickly complete station switching and angle adjustment, significantly accelerating the pace of welding operations and meeting the requirements of high-volume, high-efficiency production line welding.
Employing high-precision gear grinding technology, the spur gear slew drive achieves a transmission accuracy of 0.04 mm, enabling precise positioning and smooth rotation of robot welding torches. In scenarios such as complex weld seam welding and high-precision butt welding, it can effectively avoid welding quality issues caused by positioning deviations, ensuring uniform and strong weld seams, greatly improving product welding qualification rates, and is particularly suitable for the precision welding needs of high-end equipment.
The spur gear slew drive adopts a highly integrated design, integrating core components such as transmission gears, bearings, and sealing structures into a single unit. Compared with traditional split-type transmission systems, its volume is reduced by more than 35%, significantly saving installation space. This not only lowers the overall layout difficulty of welding robots but also adapts to the flexible deployment needs of narrow welding stations. Meanwhile, it simplifies the installation process, shortens the equipment commissioning cycle, and reduces production line construction and maintenance costs.
In semiconductor packaging and testing lines, the die insertion machine is a key device that enables precise alignment between chips and carriers. Its operational accuracy and speed directly determine the yield rate of chip packaging and the efficiency of the production line.
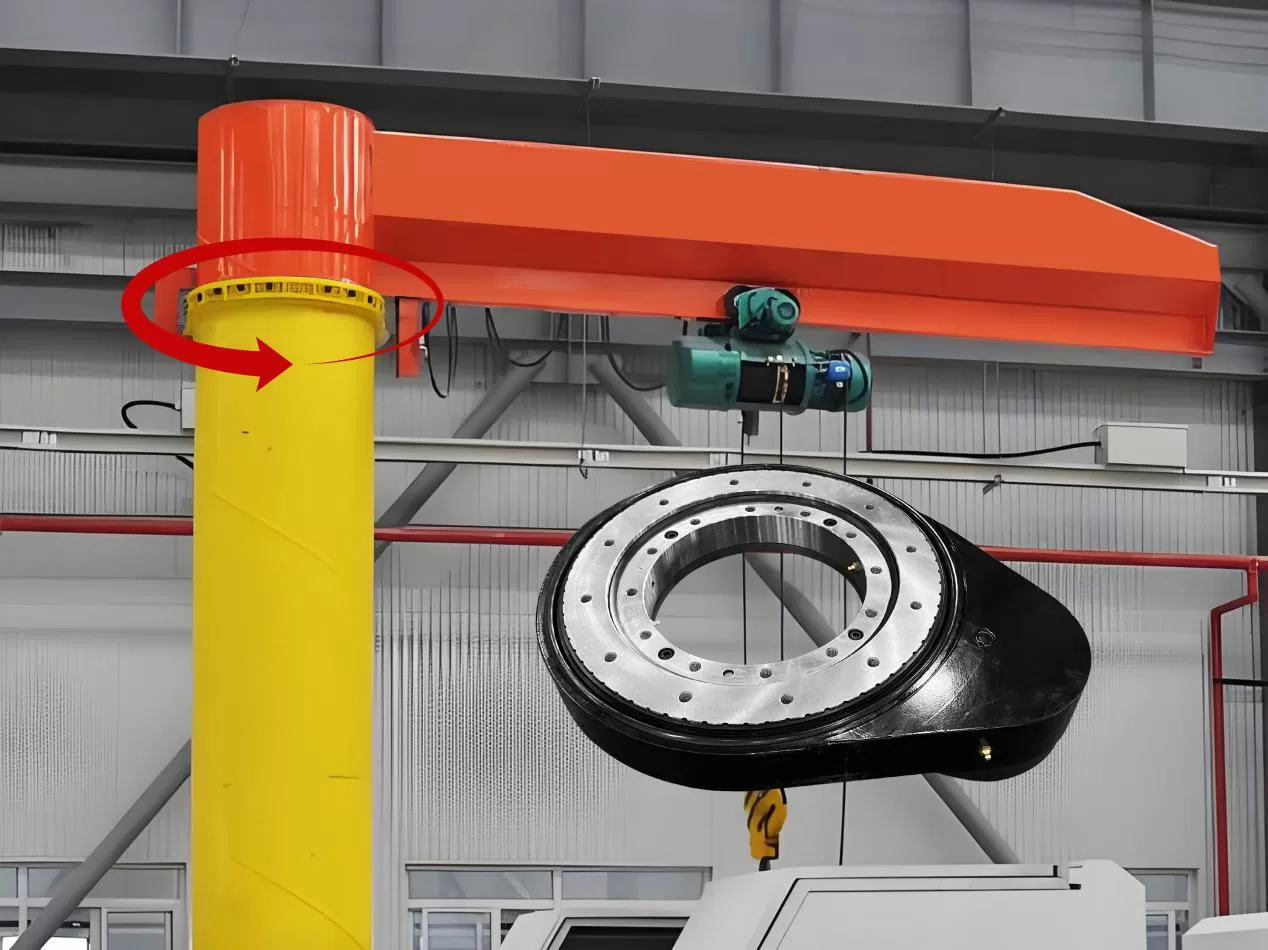
In scenarios such as workshop material handling and equipment maintenance, the stable operation of jib cranes is directly related to lifting safety and operational efficiency — and the key to supporting the precise and reliable rotation of their boom is the spur gear slew drive system integrated into the base.
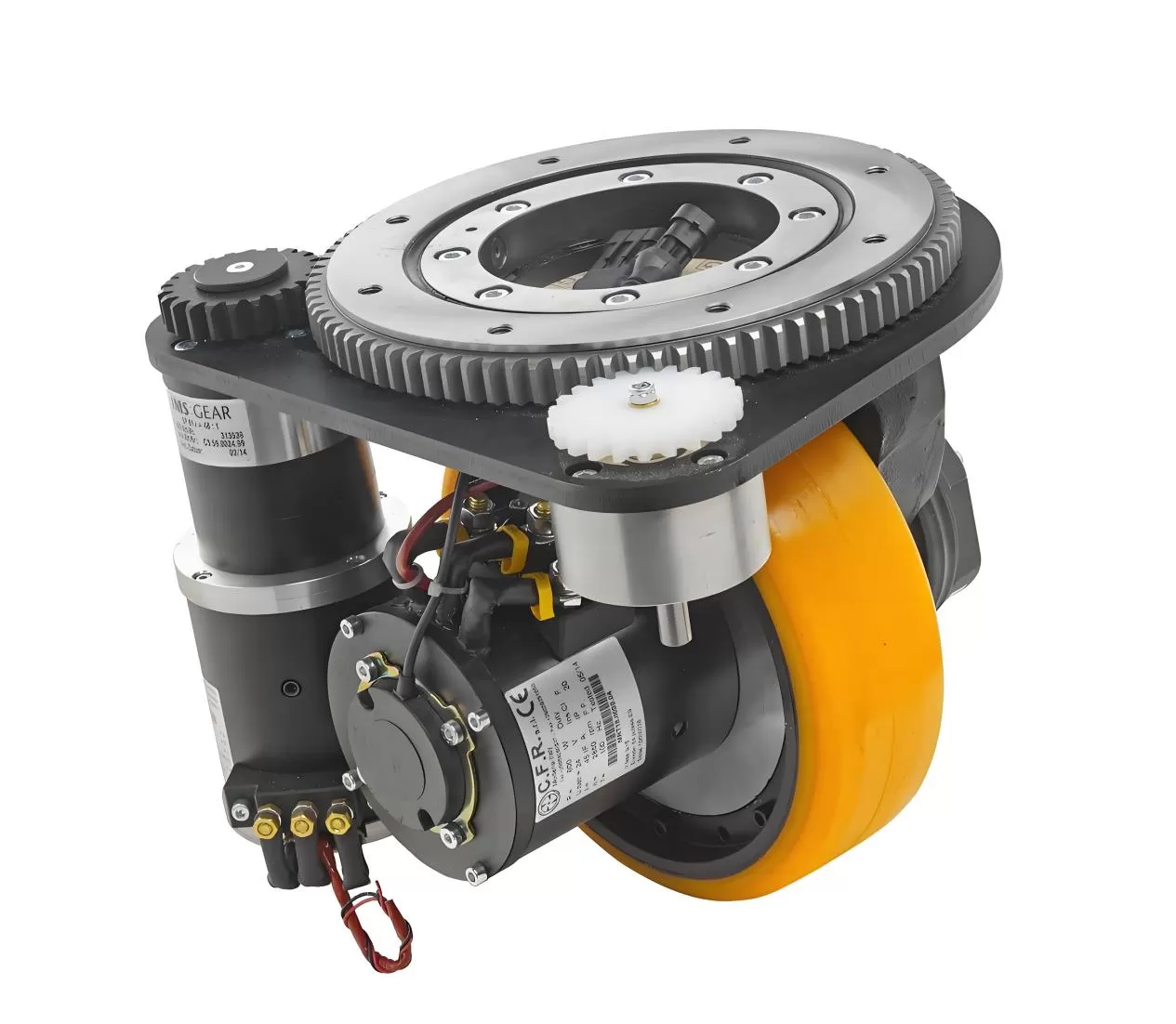

The spur gear slew drive adopts a precision tooth profile design combined with a gear grinding process, with the transmission backlash controlled within 0.02 mm. When integrated with the steering mechanism of the drive wheel, it enables the AGV to achieve a steering accuracy of ±0.5° — even in narrow passages, the AGV can travel precisely along the preset path, avoiding frame collisions and path deviations.

Small-module Tooth Profile DesignThe spur gear slew drive adopts an optimized small-module tooth profile design. Compared with traditional large-module gears, small-module gears feature smaller tooth pitches and a greater number of teeth, enabling tighter meshing during transmission and minimizing transmission backlash to an extremely narrow range.
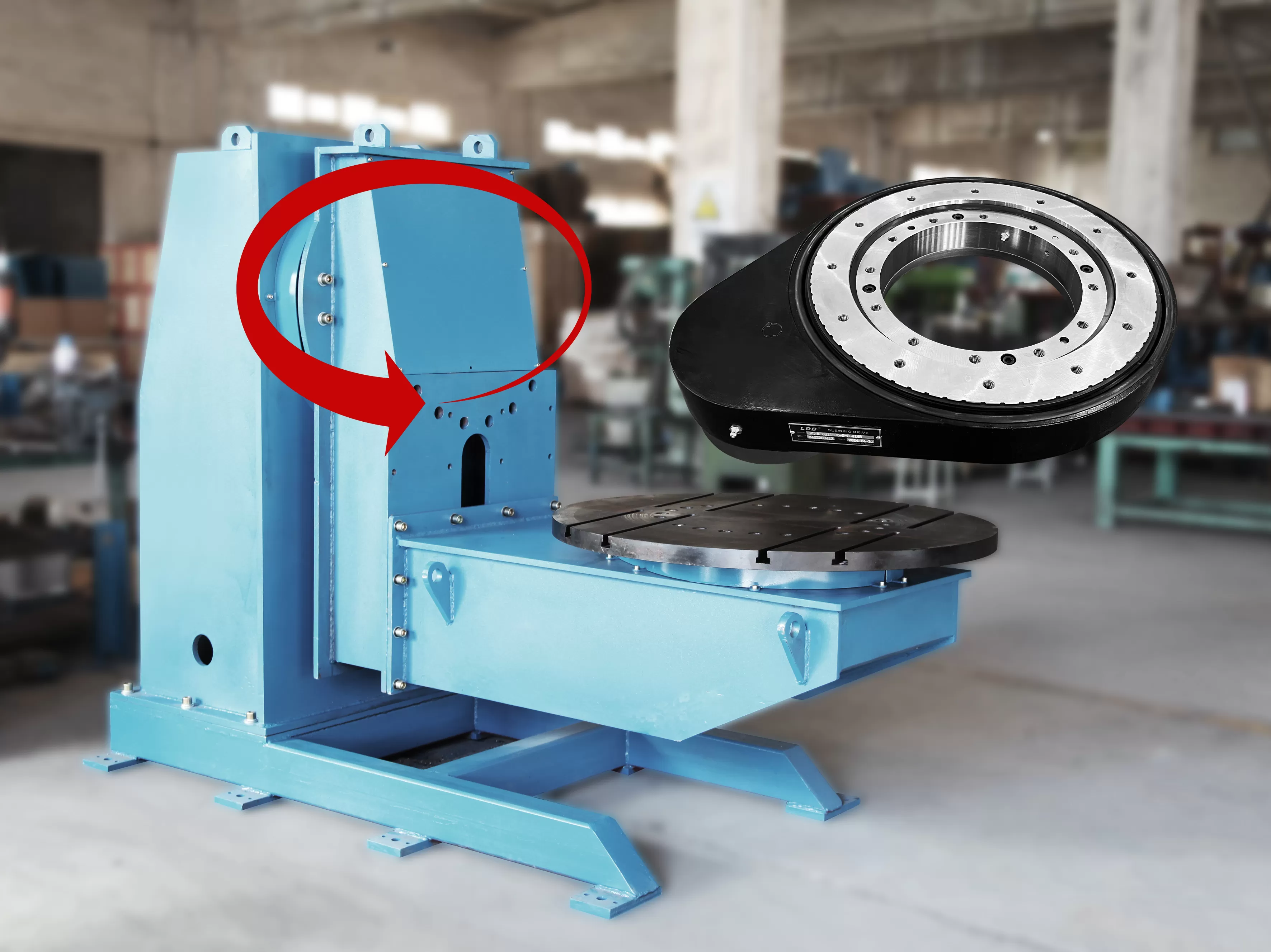

In the field of precision mechanical processing, the positioner is a key auxiliary device for achieving multi-face workpiece machining and improving processing efficiency. Its tilting accuracy, load-bearing capacity, and operational stability directly determine the machining accuracy of workpieces and the continuous operation efficiency of production lines.
Chat Online
Get A Quote
We value your feedback! Please complete the form below so that we can tailor our services to your specific needs.